
Win98 and ICS
Whilst ICS is not the most functional of methods available for Internet Sharing, it has the advantage that it is relatively easy to set up and is free. Quite a number of folks use it quite happily but it can cause performance problems and can be a pain to set up for unusual TCP/IP ports for software such as games, PCAW and VPN services, for example.
System Requirements
System requirements for ICS vary. It is possible to run it on a relatively low-spec machine such as a 200 or 300MHz machine, but use the PC for anything else and network response will suffer, both for the ICS machine itself and for all the clients using it for Internet services. Having said that, faster machines can also suffer with performance problems when using ICS, again more so when the machine running ICS is used as a workstation as well.
In order for your PC to be used for ICS with a Cable Modem, the PC needs to have two ethernet cards installed. One connects to the Cable Modem and the other connects to your local network by whatever architecture being used. The Modem connected interface should be set for TCP/IP protocol only and should be set to get an IP address automatically. The Network facing NIC requires manual setting to have the address 192.168.0.1 with a subnet mask of 255.255.255.0, but it can also have other services installed as well, such as Microsoft Networking if required. All of the client PCs are required to automatically get their TCP/IP address, which they will get from the ICS DHCP server running on the gateway PC.
The following diagram shows logically how everything connects together in an RJ45 environment.
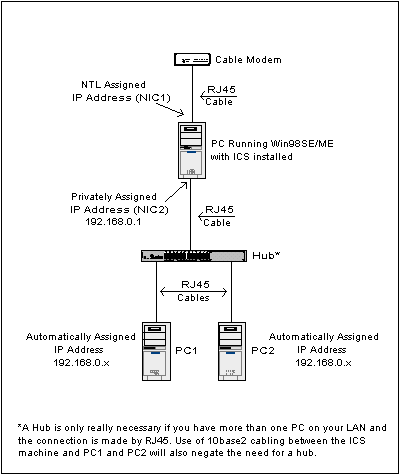
If you only have one PC to connect with the ICS gateway, the PCs can be connected together using an RJ45 Cross-over cable (assuming RJ45 is being used).
IP Address Configuration
There are three separate TCP/IP configurations you need to consider:
- ICS PC to Cable Modem
In Control Panel, dbl-click on the Network Icon, or right-click on Network Neighborhood on the desktop and select Properties. Select Properties for the TCP/IP settings for the NIC connected to your modem. Ensure that:- IP Address is set to 'Obtain an IP address automatically'.
- DNS is disabled
- There are no Gateways set.
- ICS PC to Local Network
Using the same methods outlined above, select the interface connected to the local network. Ensure that:- IP address is specified as 192.168.0.1 with a mask of 255.255.255.0
- DNS is disabled
- There are no gateways set
- Network PC
Any PCs attached to the Network should have the same settings shown, which are actually identical to the Modem connected NIC in the ICS machine. Note, however that the client PCs will probably not find an address until ICS is set up and running on the gateway.- IP Address is set to 'Obtain an IP address automatically'.
- DNS is disabled
- There are no Gateways set.
Setting up ICS on the Gateway PC
In order to set up ICS on the Gateway machine, run the ICS Networking Wizard, which configures ICS based on the responses given. The first screen is the introduction:
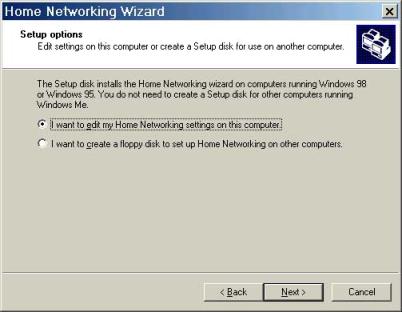
And the second asks whether to change the Home Networking settings, or to create a boot disk. Select the Home Network Settings, and the wizard will continue through the settings.
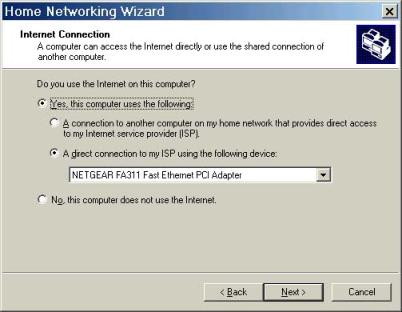
The next screen asks whether ICS should be set up for a server or client. Select Direct Connection to ISP and select the adapter to use. This must be the adapter that is connected to the Modem.
If you are setting up a Client PC, then select Connection via another PC on the Network.
Set the next screen to determine the Local Network connection and to enable it for Internet Sharing. Again, it is important to select the correct interface.
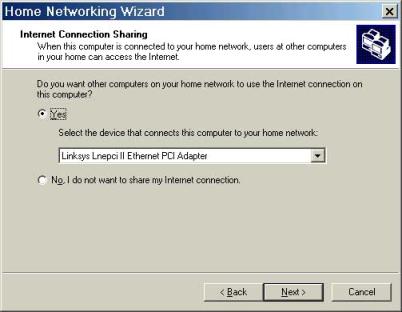
The following two screens determine the Microsoft Network options that you want to set on the Local Network. If the default Workgroup name is kept, that all devices on the local network need to be in this workgroup as well.
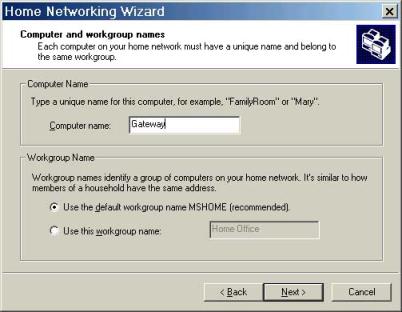
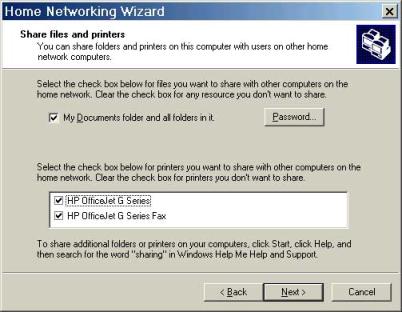
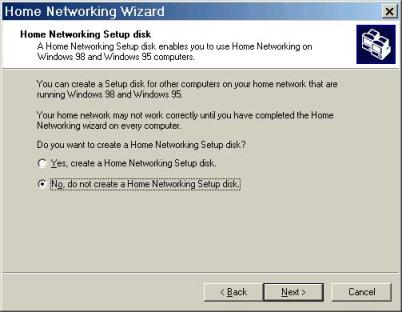
Finally, the ICS wizard asks if you wish to create an ICS startup Disk. Select yes, only if you want to create one, otherwise, selecting 'No' finishes the ICS Wizard.
Testing Everything Works
Once the Gateway PC is rebooted the first thing to check is that an IP address has been set on the Modem connected adapter - run winipcfg from the Start/Run dialog box. If this has an IP address that starts with 169, then the address negotiation failed and Windows has allocated a default. This should only really occur if the NIC attached to the CM has physically changed. In this case, power off the modem, then turn it back on again. Wait for it to negotiate with the head-end and then reboot the gateway machine.
Assuming that the connection from Gateway to Internet is correct, then boot up one of the client PCs. Again, use winipcfg (or whatever utility is available on the OS of the client PC) to check that an address of 192.168.0.x is set, where x is any number from 2 to 254. If this is the case then try pinging the gateway machine using ping 192.168.0.1 from a DOS command prompt.
If the local Ping works, then, from the client, try pinging a site on the Net, for instance ping www.bbc.co.uk. If this responds OK, then it should be just a case of running your browser in order to use the Net from the Client PC
.
All Copyrights and Trademarks ACK'd. Not to do so would be a SYN!